Microbiological validation of sterilization processes

Increase the safety of your products with microbiological validation
Filling food and cosmetics hygienically and safely is a challenge in many cases, but is crucial to the quality and shelf life of the end product. To support you in this, we offer comprehensive microbiological validation of your sterilization processes and aseptic lines so that packaging and filling processes can be designed safely and resource-efficiently.
Microbiological challenge tests to identify weak points in the sterilization process
We use microbiological challenge tests to validate the effectiveness of your sterilization process (e.g., for food or packaging materials) and identify potential weak points or areas for optimization. To do this, we use process-specific bioindicators, which are individually produced using customized contamination methods and resistance-tested test organisms. By combining specific test organisms with practical test conditions, we create the basis for reliable and meaningful results.
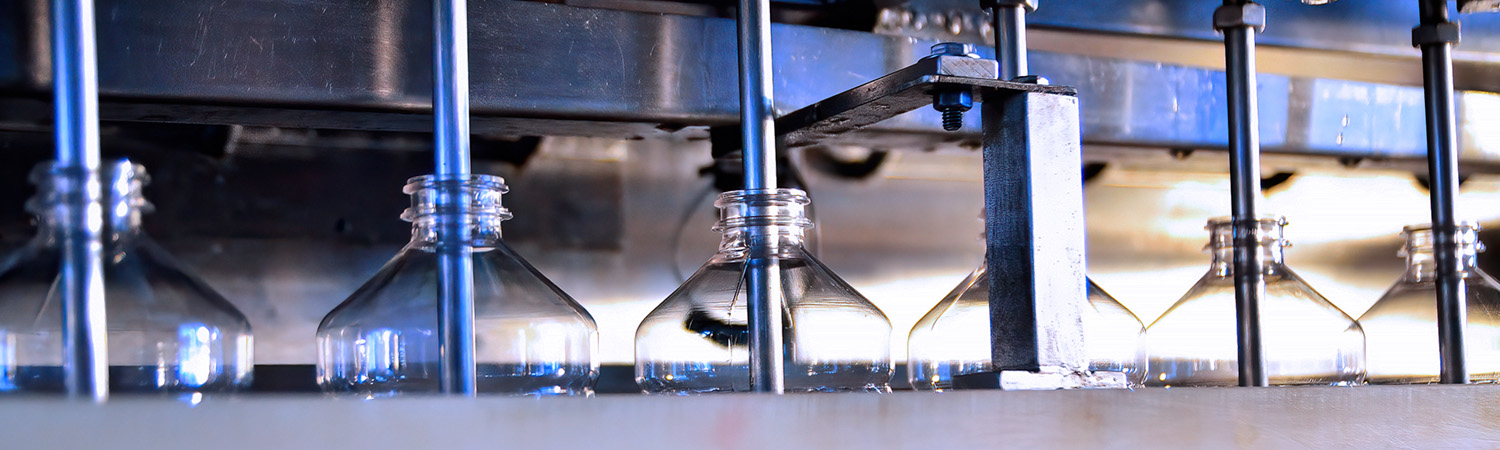
Validation of sterilization processes for packaging and systems
We also advise on process optimization and system design
Using defined test organisms, we precisely quantify the inactivation efficiency of your packaging and machine sterilization. For this purpose, bioindicators (artificially contaminated carrier materials such as packaging or machine parts) are introduced into the real process. Based on the results of the microbiological validation, we advise you on process optimization and system design. At the same time, we provide you with microbiological proof of efficacy in accordance with the recommendations and information sheets of the VDMA.
Regular tests and inspections help to assess the functionality of filling systems and to identify potential weak points. They also provide transparent evidence for audits and documentation.
Our service portfolio for validation
- Verification and quantification of the performance of different disinfection processes in accordance with VDMA recommendations
- Identification of potential microbiological hazards in the process chain as early as the development phase, during commissioning on site and during revalidations
- Inspection of system sterilization (sterilization-in-place)
- Location-resolved verification of sterilization performance
- Development of specific, resistance-tested bioindicators
- Microbiological packaging material tests
- Advice on the development of sterilization systems
Challenge tests for the validation of heating processes
We use microbiological challenge tests as an important tool to validate and verify the effectiveness of heating processes in food production. In this way, we ensure that potentially pathogenic microorganisms are reduced to a safe level by heating and that product safety and shelf life are guaranteed. The product is specifically inoculated with relevant microorganisms (e.g. Salmonella, Listeria) under controlled conditions to test the inactivation of these pathogens by the specific heating process in the specific matrix.
Influence of food properties
The need for microbiological challenge tests arises from the fact that the composition and properties of the food (such as pH, sugar content, salt content, protein content, etc.) can strongly influence the D and z values of microorganisms. A challenge test examines the mortality behavior of microorganisms in the food matrix under standardized, practical conditions.
Challenge tests result in critical control points
The results (D and z values) of a challenge test provide information on the temperature and duration of the heating process required to achieve the desired microbial reduction. The data obtained helps to define critical control points as part of HACCP concepts and to confirm that the heating process is sufficiently robust to minimize potential microbiological risks. It is also possible to optimize oversized heating processes to save energy.
Special hot water autoclave creates realistic test conditions
We use a special hot water autoclave to realistically simulate industrial heating processes on a laboratory scale. In microbiological challenge tests, this allows us to precisely determine the relevant process parameters, such as treatment temperature and treatment duration, under realistic and controlled conditions. On this basis, we can validate heating processes for safe and gentle treatment of products.
Our service portfolio for challenge tests
- Isolation and identification of microbial contaminants
- Support in determining the cause of microbial contamination
- Determination of D and z values of relevant microorganisms in the product matrix
- Artificial bacterial contamination of food products for challenge testing, including apathogenic surrogates
- Evaluation of heating processes for packaged products on a laboratory scale by practical simulation of the real heating process
- Identification of potential microbiological hazards in the process chain during development, on-site commissioning and revalidation
- Assessment of the overall hygienic condition of the operating rooms
- Determination of the causes of complex failures
 Fraunhofer Institute for Process Engineering and Packaging IVV
Fraunhofer Institute for Process Engineering and Packaging IVV